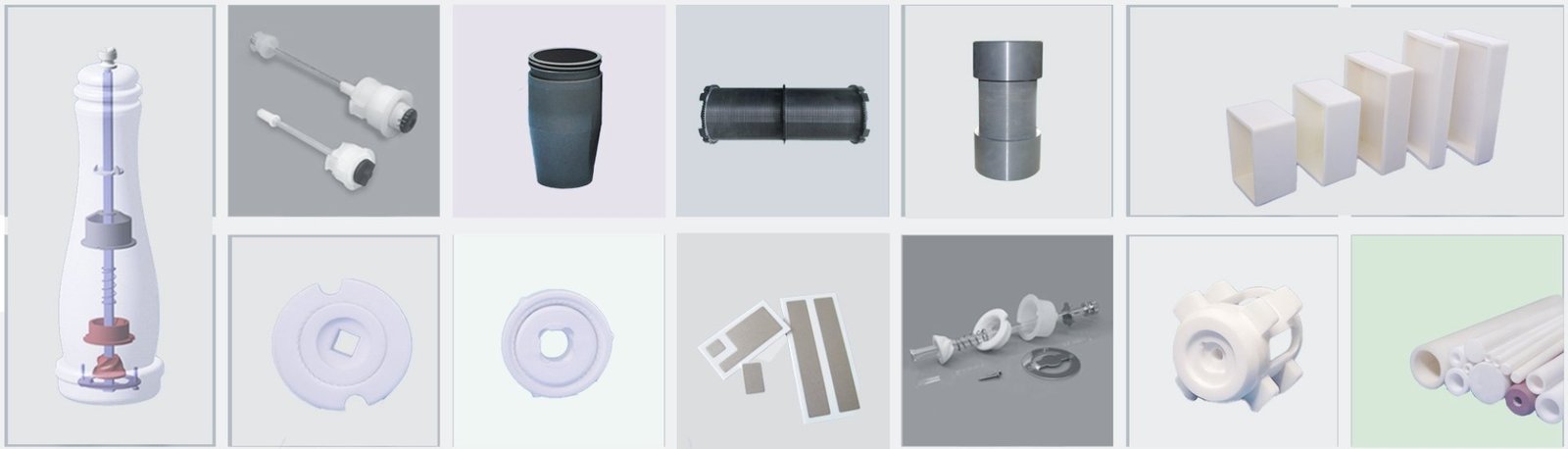
In the ceramic industry, there are significant differences between traditional ceramics and advanced ceramics. These differences are not only reflected in the material properties, but also determine their respective application areas and market value. This article will give you a deep understanding of these two types of ceramics.
Definition of Traditional Ceramics and Advanced Ceramics
1. Traditional Ceramics
Traditional ceramics have a history of thousands of years, dating back to the Neolithic Age. It is a silicate product made of natural clay as the main raw material, which is formed, dried and fired. Common traditional ceramics include building ceramics and daily-use ceramics.
2. Advanced Ceramics
Advanced ceramics are a new type of ceramic material developed in the mid-20th century, also known as “fine ceramics” or “technical ceramics”. It uses artificially synthesized ultra-fine high-purity powder as raw material and is prepared through precision control technology. It has special properties that traditional ceramics cannot match.
The Main Differences Between Traditional and Advanced Ceramics
The main differences between traditional and advanced ceramics lie in their raw materials, manufacturing processes, performance characteristics, and application areas.
1. Raw Materials
The raw materials for traditional ceramics mainly come from natural minerals such as clay, quartz, and feldspar. They are mainly silicates and contain a large amount of impurities (such as Fe2O3, CaO, etc.). They have general chemical stability and may undergo phase transformation or decomposition at high temperatures.
Advanced ceramics use artificially synthesized ultra-fine powders, such as oxide ceramics (Al2O3, ZrO2, etc.) and non-oxide ceramics (such as SiC, Si3N4, AlN, etc.). Their raw material costs are higher, but their performance is controllable, such as through doping modification (e.g., Y2O3-stabilized ZrO2) to enhance toughness.
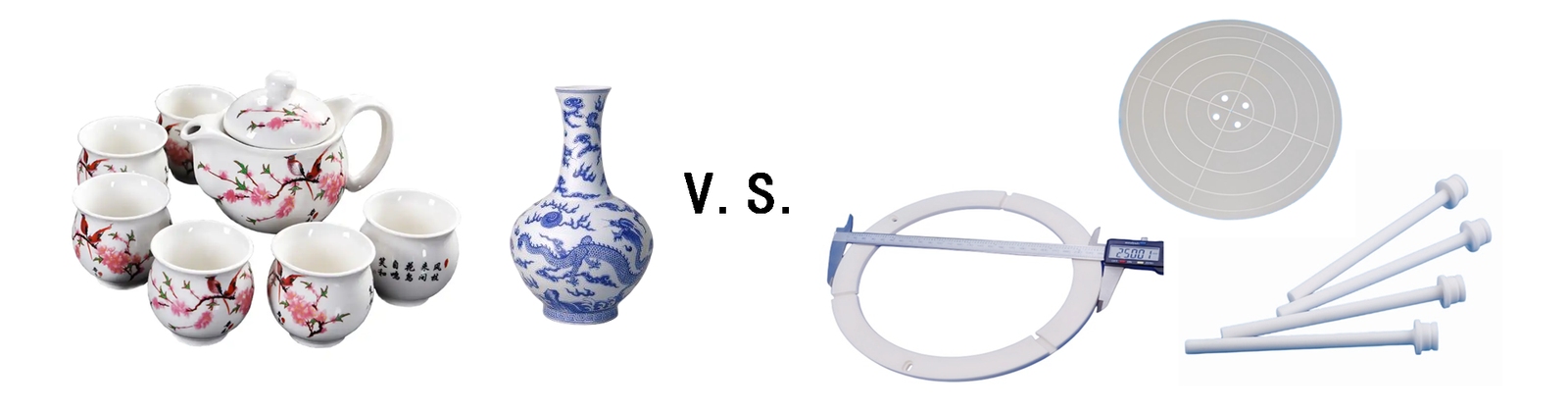

Traditional Ceramics Vs. Advanced Ceramics
2. Manufacturing Process
Traditional ceramics are mostly formed by grouting, slurry molding or mud plastic molding. It usually does not require additional processing after high-temperature firing. However, the manufacturing of advanced ceramics is more complicated. Its common forming methods include dry pressing, hot pressing, isostatic pressing, tape casting, extrusion and injection molding. And it may require additional post-sintering processing to achieve ultra-high precision and performance optimization.
3. Performance Characteristics and Application Areas
Through the comparison in the table below, we can clearly see the key differences between traditional and advanced ceramics in terms of their essential properties.
| Comparative Item | Traditional Ceramics | Advanced Ceramics |
| Raw Material | Clay, quartz, and feldspar | Synthetic powder (e.g., Al2O3, ZrO2, etc.) |
| Purity | Containing a high amount of impurities | Usually with high purity |
| Manufacturing Process | Simple forming, firing at 800-1200℃ | Precision forming, sintering at 1400-2000℃ |
| Precision Machining | Not suitable | Suitable |
| Microstructure | Coarse grains and many pores | Small grains and dense structure |
| Mechanical Strength | Low, brittle | Very high, some comparable to metal |
| High Temperature Resistance | Limited | Excellent |
| Application | Building ceramics such as tiles, bathroom fixtures, and refractory bricks, and daily-use ceramics such as tableware and decorative items. | Used in extreme environments, high-precision applications, or special functions (such as semiconductors and medical implants). Typical application areas include the electronics industry, medical field, aerospace, and new energy. |
Conclusion
Traditional ceramics and advanced ceramics each have their own unique value and scope of application. Traditional ceramics, with their economic advantages and mature manufacturing processes, continue to play an irreplaceable role in daily life and basic industries. Advanced ceramics, on the other hand, with their outstanding performance, have become key materials supporting the development of high-tech industries.