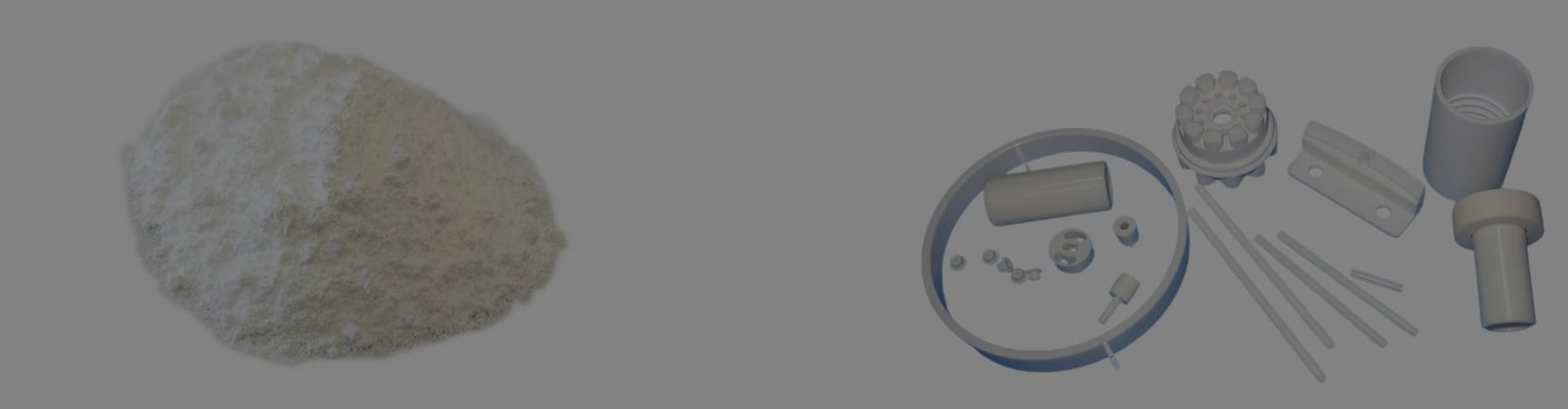
Material Overview
Alumina, short for aluminum oxide (Al2O3), is an advanced ceramic material with excellent mechanical and electrical properties. Due to the abundant raw material resources and mature extraction and purification technologies of aluminum oxide, it is widely used across many fields, including electronics & electrical, automotive, medical, semiconductors, and more.
Alumina is the “tough guy” among industrial ceramic materials. It offers exceptional hardness, high wear and high-temperature resistance, and excellent insulation properties, while operating reliably in aggressive chemical environments. Furthermore, its biocompatibility is impressive. Alumina’s performance varies primarily with its purity and the additives used; higher purity is associated with better mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties.
Physical properties
| Property | Units | 99.8% Al2O3 | 99.5 Al2O3 | 99% Al2O3 | 96% Al2O3 |
| Density | g/cm3 | ≧3.92 | ≧3.90 | ≧3.80 | ≧3.65 |
| Vickers Hardness | HV | ≧1700 | ≧1570 | ≧1520 | ≧1380 |
| Compressive Strength | Mpa | ≧2650 | ≧2240 | ≧2160 | ≧2068 |
| Flexural Strength | Mpa | ≧400 | ≧350 | ≧310 | ≧280 |
Thermal properties
| Property | Units | 99.8% Al2O3 | 99.5 Al2O3 | 99% Al2O3 | 96% Al2O3 |
| Max. Service Temperature (Non-loading in the air) | ℃ | 1750 | 1700 | 1600 | 1500 |
| Thermal Conductivity(25℃) | W/m.k | ≧32 | ≧30 | ≧29 | ≧24 |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion(20-800℃) | 1×10-6/℃ | 7.2 ~ 8.2 | 6.5~8.0 | 6.2~8.0 | 6.5~8.0 |
Electrical properties
| Property | Units | 99.8% Al2O3 | 99.5 Al2O3 | 99% Al2O3 | 96% Al2O3 |
|
Dielectric Strength |
ac-KV/mm | ≥20 | ≧18 | ≧17 | ≧15 |
|
Dielectric Constant (1Mhz) |
(E) | 9.8 | 9.7 | 9.6 | 9.4 |
|
Volume Resistivity @25℃ |
Ω·cm | 1*1014 | 1*1014 | 1*1014 | 1*1014 |
Alumina Productions
Initial alumina products can be shaped via injection molding, pressing, slip casting, tape casting, and extrusion. In its green or billet state, alumina is processed into complex geometries through various forming processes. The initial molded products are then sintered to solidify the structure. The sintered ceramic parts are further precision-machined using diamond grinding to meet the customer’s technical specifications. You can connect alumina products to metals or other ceramics using metallization and brazing technologies.
Among alumina ceramic products, the most commonly used forms are plates, rods, substrates, metalized alumina ceramics, and tubes. These products fully leverage aluminum oxide’s excellent properties. The following product examples show other forms.
-
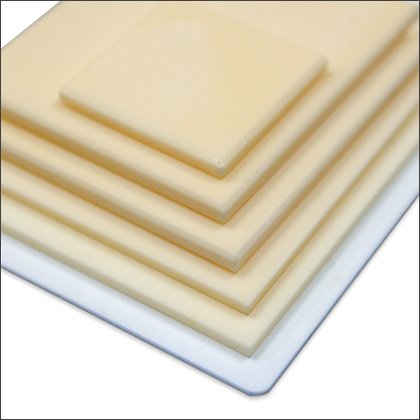 Alumina Sheets
Alumina Sheets -
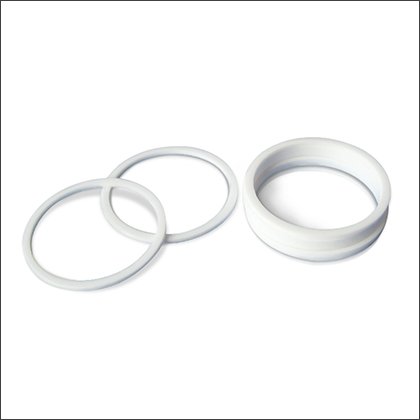 Alumina Rings
Alumina Rings -
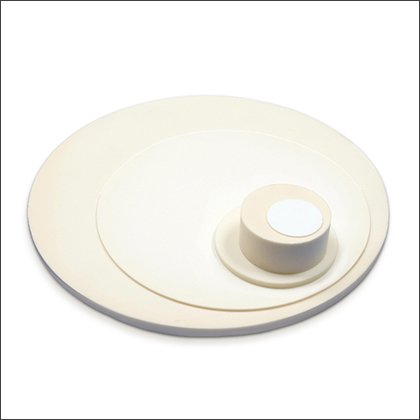 Alumina Discs
Alumina Discs -
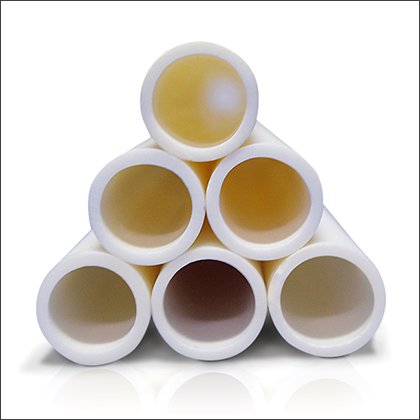 Alumina Tubing
Alumina Tubing -
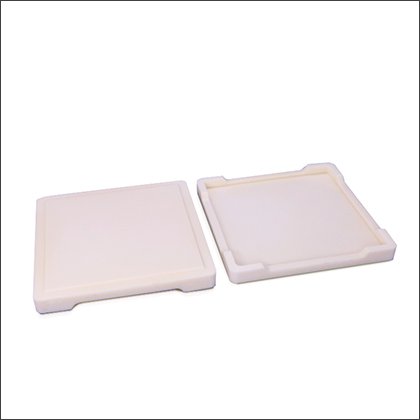 Alumina Trays
Alumina Trays -
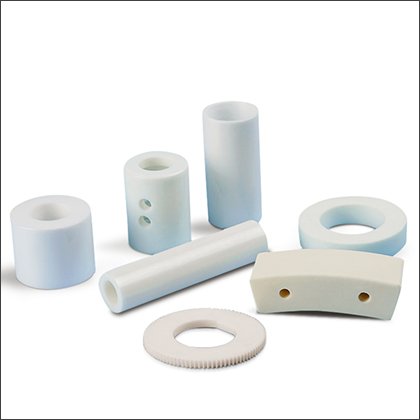 Alumina Parts
Alumina Parts
Related Materials
-
Zirconia ceramics are second only to alumina ceramics in terms of applicability and are very important advanced ceramics for structural applications.
-
Aluminum nitride ceramics are advanced ceramics with high thermal conductivity and insulation, and are often used in electronic packaging substrates and heat dissipation components.
-
Silicon nitride ceramics are high-strength, lightweight, and thermally shock resistant advanced ceramics commonly used in bearings and turbine components.
-
Steatite ceramics are low-cost, high-frequency insulators, and have low mechanical strength, making them suitable for use in general equipment parts.
-
Cordierite ceramics have ultra-low thermal expansion and are resistant to thermal shock, making them suitable for use as catalyst carriers and thermal insulation materials.
Key Strengths
Aluminum oxide has a very stable crystal structure and advanced preparation technology. Its balanced physical, chemical, mechanical, and electrical properties make it the “economical champion” of advanced ceramics.
1. Cost
Much lower than fine ceramic materials such as zirconia, silicon nitride, silicon carbide, and aluminum nitride.
2. Electrical insulation
Better than silicon carbide and silicon nitride, and comparable to zirconium oxide.
3. Hardness/wear resistance
Mohs hardness is 9, second only to diamond and cubic boron nitride among known materials.
4. Chemical stability
It will not react chemically with most acids, alkalis, and molten metals
Alumina Uses
● Electronics
Thanks to its remarkable electrical insulation and ideal thermal properties, it’s widely used as a raw material for insulators, power substrates, and protective films.
● Abrasive Materials
Due to aluminum oxide’s superb wear resistance, it’s usually used as the material of grinding media, industrial ceramic tiles, ceramic coatings, and diamond sandpapers.
● Refractories
Because of their high-temperature resistance and thermal stability, they are commonly used as furnace linings, kiln linings, and incinerator linings.
● Engineered Ceramics
Considering its well-balanced properties and cost-effective benefits, it’s one of the most versatile engineering ceramics, used in alumina cores, ceramic seals, pump components, and more.
● Biomedical
Given alumina’s biocompatibility and resistance to wear, it’s a proven material to use to make medical devices like hip replacements and dental implants
Manufacturing & Customization
● Advanced Processing
Jinghui Ceramic is skilled at producing precise, complex industrial alumina ceramic parts. They use advanced manufacturing methods like multi-axis machining, drilling, grinding, milling, polishing, sawing, tapping, thread processing, and turning. These methods help meet strict requirements for shapes, tight size tolerances, and surface treatments of your ceramic products.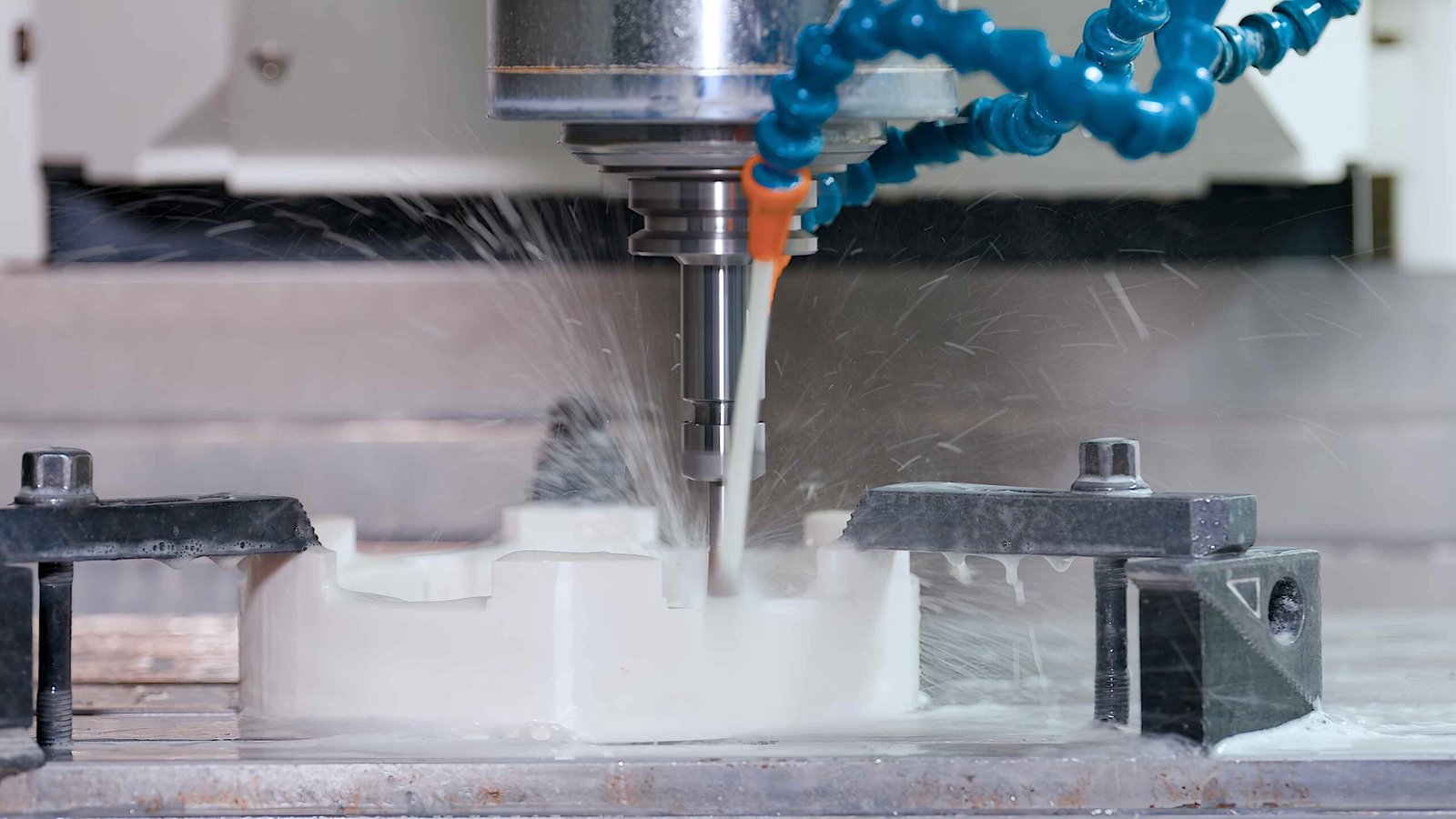
● Customization
We can offer customized formulas to meet specific functional, performance, and appearance needs, such as doping different metal elements or compounds as additives into alumina. In addition, mini-size (OD to be 0.80mm) to large-size ( OD to be 300mm) parts are within the capability. What’s more, like metalizing, polishing, glazing, and the diversity of surface finishes, can be carried out at home.
What is more, we offer technical consultation, guiding material selection, and part design. We are eager to jointly develop the next generation of products with our esteemed customers to meet their increasingly demanding application requirements.
Because alumina contains the metallic element aluminum, some people mistakenly think of “alumina” as “metal.”
Actually, alumina and metal are fundamentally different:
- Alumina is an inorganic, non-metallic ceramic that serves as an excellent electrical insulator.
- Alumina is extremely hard and brittle, lacking the ductility of metal.
- Alumina is a chemical compound made of aluminum and oxygen atoms. These atoms are connected by ionic and covalent bonds, not just aluminum.
In some industrial fields, such as metallurgy and the wear-resistant industry, alumina is commonly referred to as “bauxite,” leading those unfamiliar with the ceramic material to naturally associate it with metal.
High-purity (purity above 99%) polycrystalline alumina ceramics are pure white.
However, to meet specific functional or aesthetic requirements, designated metallic colorants are added to the ingredients, resulting in different colors for the alumina product. For example,
1) Adding a certain proportion of manganese oxide results in a black ceramic.
2) adding a certain proportion of chromium oxide results in a red/rose ceramic;
3) Adding a certain proportion of cobalt oxide results in a blue ceramic.
Alumina ceramics do not have just a single color. Their color mainly depends on purity and the colorant used.
The chemical formula Al2O3 is aluminum oxide, also known as alumina. The most common name also has some nicknames and professional names. These names depend on their forms, crystal shapes, and uses. Its mineral name is corundum. In industry and materials science, it can be called bauxite or activated alumina.
Alumina is a compound made of two aluminum (Al) atoms and three oxygen (O) atoms. Its chemical formula is Al2O3. It is the most stable form of aluminum on Earth.
No, alumina is not only non-flammable, but also a flame retardant and refractory material with high temperature resistance and high melting point; In industry, alumina is often used as crucibles and linings in steel smelting furnaces.
In modern industry, alumina is produced primarily through three methods: the alkaline process, the acid process, and the thermal process.
The alkaline process is the primary method for producing alumina. It includes the Bayer process, the soda-lime sintering process, and the combined process. The Bayer process accounts for approximately 90% of global alumina production capacity. It uses high-grade bauxite (Al₂O₃/SiO₂>7) and dissolves the alumina in sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to produce a sodium aluminate solution, which is then decomposed and calcined to produce alumina.
Alumina is a safe industrial ceramic material. The sintered ceramic products used in industry and daily life are not toxic. The material is considered an indirect additive used in food contact substances by the FDA.
Its main toxicity is related to occupational dust inhalation or dust in the eyes. As long as you don’t breathe in the powder and keep the dust out of your eyes, alumina is not very harmful.
The following mainly describes the differences between the three from the intrinsic properties:
Alumina: The backbone of the advanced ceramic family, it has high hardness, wear resistance, stability, and insulation, but it is prone to brittle cracking when encountering substantial impact.
Zirconia: The key features of the family are its exceptional toughness, high strength, and biocompatibility.
Zirconia-toughened alumina is abbreviated as ZTA. A certain proportion of zirconium oxide is added to alumina (typically, the content of zirconia is within 10% ~20%). Therefore, this material incorporates the excellent genes of zirconium oxide into alumina. It inherits alumina’s toughness and zirconium oxide’s flexibility.







