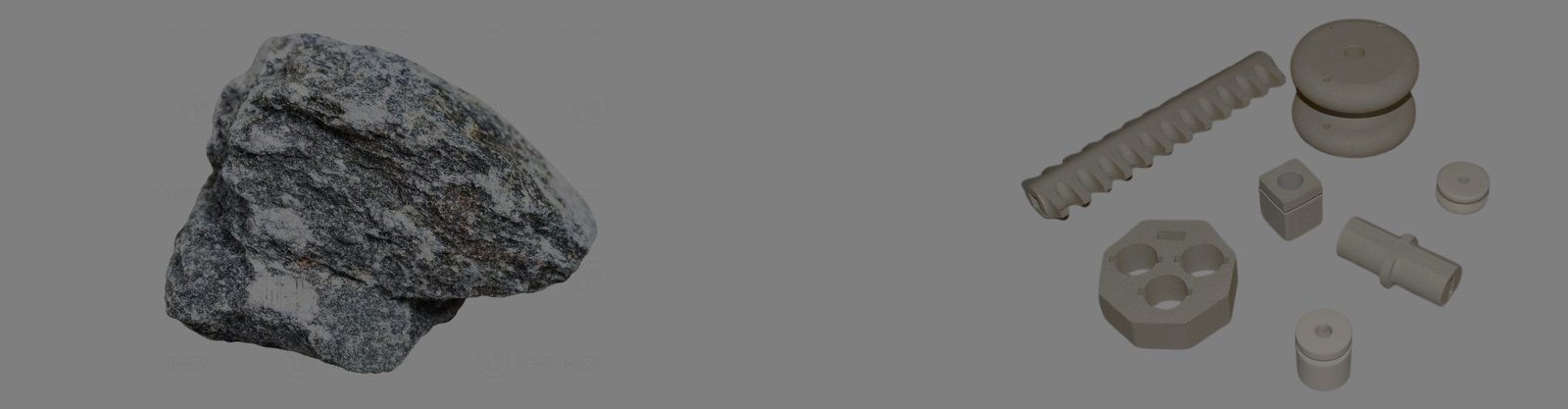
Material Overview
Steatite, a magnesium silicate ceramic, molecular formula is 3MgO.4SiO2.H2O,its color is usually white or beige. It is composed of a variety of chemical components, the contents of which are shown below:
| [Steatite powder]Content of chemical composition (%) | |||||
| Chemical Element | Fe2O3 | MgO | CaO | TiO2 | Al2O3 |
| Inspection standard | <0.5 | 29-32 | <0.8 | <0.1 | <1 |
| Chemical Element | SiO2 | K2O | Na2O | Ingition Decerement | Amount |
| Inspection standard | 59-63 | <0.5 | <0.5 | <7 | 99.5-100.5 |
Steatite is engineered for exceptional electrical insulation, thermal stability, and mechanical durability. With a density range of >2.7 g/cm³ and flexural strength >140 MPa, it outperforms traditional materials in high-temperature and high-voltage environments. Ideal for electrical enclosures, insulators, and industrial components, steatite combines cost-effectiveness with reliability in aerospace, automotive, and appliance industries.
Steatite Vs 85% Alumina Data Table
| Property | Steatite | 85% Al2O3 |
| Density (g/cm³) | >2.7 | >3.4 |
| Flexural Strength (MPa) | >140 | >220 |
| Modulus of Elasticity (GPa) | 120 | 221 |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | 2.5 | 16 |
| Max. service temperature (℃) | 800 | 1200 |
Steatite Ceramic Productions
Steatite ceramic has low cost, high-frequency insulation, and low mechanical strength. It is used in general device parts that require both cost-effectiveness, such as ceramic grinding cores, electrical terminals, and ceramic tubes. These products can have low-end alternatives.
-
 Steatite Tube
Steatite Tube -
 Steatite Ceramic Insulators
Steatite Ceramic Insulators -
 Ceramic End Cap
Ceramic End Cap -
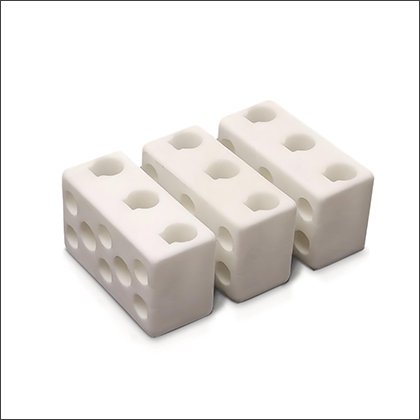 Steatite Terminal Blocks
Steatite Terminal Blocks -
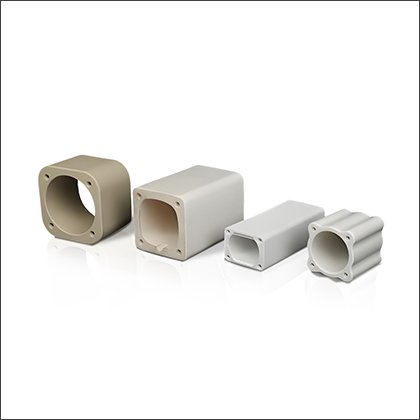 NH Fuse Ceramic Body
NH Fuse Ceramic Body -
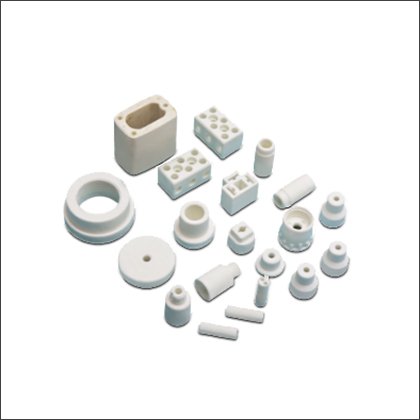 Steatite Ceramic Products
Steatite Ceramic Products
Related Materials
-
Alumina ceramics are advanced ceramics with excellent comprehensive properties, and they were researched early, are the most widely used, and are the most mature.
-
Zirconia ceramics are second only to alumina ceramics in terms of applicability and are very important advanced ceramics for structural applications.
-
The machinable ceramics have excellent machinability and can be machined using traditional metalworking tools.
-
Cordierite ceramics have ultra-low thermal expansion and are resistant to thermal shock, making them suitable for use as catalyst carriers and thermal insulation materials.
-
Mullite ceramics are resistant to high temperatures and have low thermal expansion, making them suitable for use in kiln furniture and refractory materials.
Key Features
- Electrical Insulation: Low dielectric loss and high resistivity (>10¹² Ω·cm) ensure safe operation in high-voltage systems.
- Thermal Stability: Withstands temperatures up to 800°C, making it suitable for kiln supports and heating elements.
- Chemical Resistance: Resists acids, alkalis, and organic solvents, extending lifespan in corrosive environments.
- Cost-Effective: Lower production costs compared to alumina or zirconia ceramics.
Applications
- Electronics: Insulators for circuit breakers, transformers, and sensors.
- Light: lamp cap, terminal block for lighting appliance.
- Industrial: Thermocouple protection tubes, refractory supports, and furnace linings
Steatite is the first choice for high-voltage electrical components due to its excellent insulation (high resistivity, low dielectric loss), high dielectric strength (high voltage breakdown resistance), good mechanical strength, and thermal stability. It can withstand high temperatures and mechanical stresses, has stable chemical properties, and is low-cost, making it suitable for applications such as high-voltage insulators and capacitors, ensuring safety and reliability in high-voltage environments.
Steatite resists acids, alkalis, and organic solvents due to its non-porous structure and chemical inertness. In chemical processing plants, steatite thermocouple tubes withstand exposure to sulfuric acid (pH <1) for over 5 years without corrosion. Its low thermal expansion (8 × 10⁻⁶/K) also minimizes cracking in cyclic heating applications like kiln supports.
Yes. Steatite is compatible with processes like die pressing, slip casting, and CNC machining to produce intricate geometries.








