Technical SPECs
There are three main materials (alumina,zirconia,silicon nitride) of ceramic spacers in actual use. The relevant technical specifications are as follows:
| Property | Alumina Spacers | Zirconia Spacers | Silicon Nitride Spacers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density | 3.8 g/cm³ | 6.05 g/cm³ | 3.2 g/cm³ |
| Flexural Strength | 280–360 MPa | 750 MPa | 700 MPa |
| Thermal Conductivity | 24-31 W/m·K | 2–3 W/m·K | 20 W/m·K |
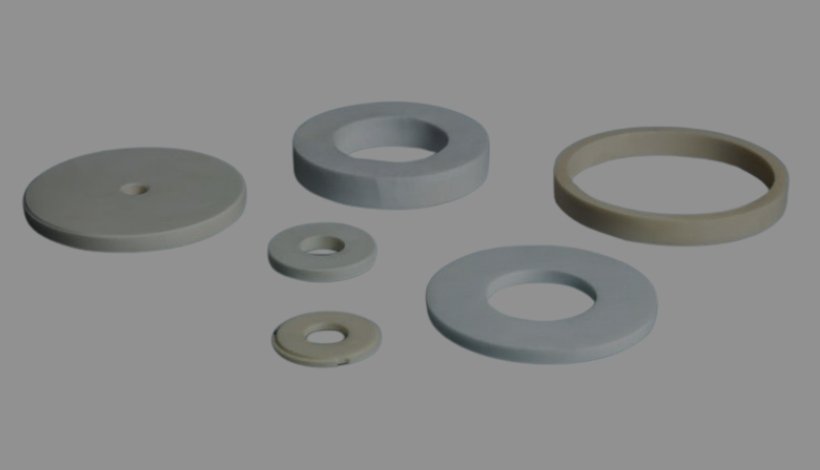
Ceramic Spacers: Precision Engineering for High-Performance Applications
Ceramic spacers are precision-engineered components made from advanced materials like alumina (Al₂O₃), zirconia (ZrO₂), and silicon nitride (Si₃N₄), designed to provide thermal stability, electrical insulation, and mechanical strength in demanding environments. These spacers are critical in industries such as semiconductor manufacturing, aerospace, energy, and medical devices, where precise tolerances and resistance to extreme conditions are essential.
Product By Features
Ceramic spacer products are customized according to customer needs. The corresponding products have different characteristics. The following are some representative products.
Flush-mount design for secure fastening in aerospace and automotive assemblies.
High dielectric strength (>15 kV/mm) for power electronics and HV transformers.
Non-reflective surface for optical equipment and laser alignment systems.
Brazable Ag/Ni coating for RF shielding and vacuum feedthrough applications.
Precision alignment (±0.01 mm) in semiconductor wafer handling robots.

High precision, small pore size, excellent thermal stability and corrosion resistance.

Cable routing and component fixation in robotics and automation systems.

Two pieces matched for a precise fit, leak-free seal and impact-resistant cushioning.
Key Features
Ceramic spacers have a wide range of applications, mainly based on several important features.
Operate continuously at 1600°C (Al₂O₃) or 1000°C (ZrO₂), ideal for high-temperature furnace components and aerospace engines.
Volume resistivity >10¹⁴ Ω·cm, preventing short circuits in high-voltage systems.
Resistant to acids, alkalis, and molten metals, ensuring longevity in corrosive environments.
The high hardness and low coefficient of friction of ceramics can reduce wear and extend the life of equipment.
Functions of Ceramic Spacers
1. Wear protection: Ceramic materials themselves have high hardness and wear resistance, which makes ceramic spacers perform well in high-speed rotating or frequently rubbing equipment parts, greatly extending the service life of the equipment.
2. Reduce vibration and noise: Ceramic spacers play a role in reducing vibration and noise in some precision instruments and equipment, thereby improving the stability and comfort of equipment operation.
3. High temperature resistance: Ceramic materials can still maintain good physical and chemical properties in high temperature environments, and will not deform or fail at high temperatures, which makes ceramic spacers an ideal sealing material in high temperature environments.
In semiconductor manufacturing, ceramic spacers (such as Al2O3, AlN, SiC) have become key components due to their ultra-high purity (no metal contamination), resistance to strong acid and plasma erosion, excellent electrical insulation, high thermal stability (low expansion + high thermal conductivity), etc. They are widely used in wafer transmission, reaction chamber sealing and heat dissipation modules to ensure process purity and equipment reliability, while metal spacers are prone to contamination and corrosion, and only a few are used in special sealing scenarios after plating.
The performance of ceramic spacers varies depending on the material.
Temperature range:
1. Conventional alumina (Al₂O₃): long-term stable operation ≤1600°C (short-term up to 1800°C).
2. Silicon nitride (Si₃N₄)/silicon carbide (SiC): extreme temperature up to 1800-2200°C (in inert gas environment).
Pressure resistance:
1. Static pressure: 50-800MPa (depending on thickness and support structure).
2. Dynamic pressure: compressive strength can reach more than 3000MPa (such as SiC).
Yes, ceramic spacers can be customized into complex geometric shapes. We can realize round or square shapes with steps, shallow grooves, special-shaped surfaces, gears, multiple holes, etc. Complex designs need to be combined with post-processing (such as laser cutting) to further improve accuracy.
-
Energy: Si₃N₄ spacers in solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs) reduce interfacial resistance by 40%.
-
Automotive: Lightweight spacers for high-temperature sensors in hybrid engines.
-
Industrial: Wear-resistant spacers in chemical pumps handling H₂SO₄.







